Key Takeaways
Shift in Adoption Patterns: Initially aimed at empowering citizen developers, the LCAP market has seen a shift. Despite initial hurdles with adoption due to the complexity of no-code tools and reliance on professional development teams, there's been an uptick in organizations successfully self-building complex applications. This change has been particularly notable in the APAC and LATAM regions, driven by a lack of local support from larger US and EU technology vendors.
Generative AI Integration: LCAP vendors are increasingly incorporating generative AI into their platforms, either by embedding the technology directly or planning to add it. This integration serves two primary purposes: enhancing the development process with AI-enabled tools and deploying applications that utilize generative AI for various functions, such as creating chatbots or generating text for emails and product descriptions. This trend is pushing the boundaries of what can be developed with LCAP tools.
Increased Application Complexity: The scope and complexity of applications developed using LCAPs have grown, with platforms now being used to create comprehensive solutions like ERP systems, payroll systems, and customer portals. This evolution indicates that low-code and no-code tools are increasingly viable for developing enterprise-grade applications.
ERP and CRM Platform Convergence: ERP and CRM vendors are rapidly enhancing their low-code capabilities, narrowing the functional gap with dedicated LCAPs. This development suggests a trend towards the integration of low-code tools within broader enterprise platforms, offering a compelling reason for organizations to consider their existing ERP or CRM tools for low-code development before seeking external solutions.
Distinct Advantages of Dedicated LCAPs: Despite the convergence of capabilities, dedicated LCAPs retain unique advantages, especially in terms of deployment flexibility and the ability to monetize applications on a global scale. Additionally, features like process mining, which facilitates continuous improvement and performance analytics, offer further differentiation for LCAPs in enhancing workflow design and operational efficiency.
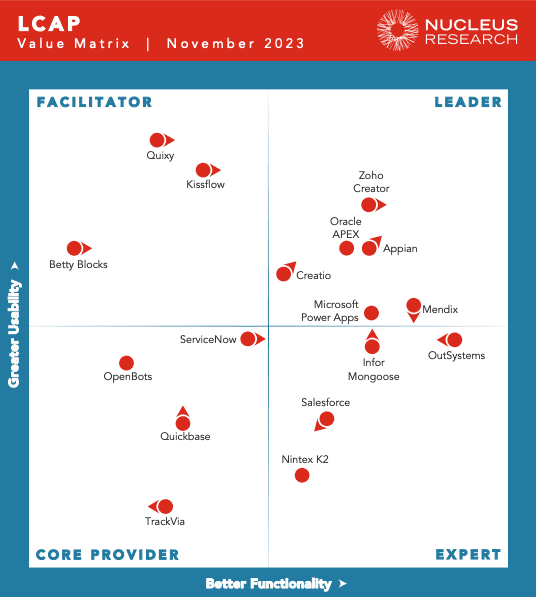
Value Matrix Insights: The Technology Value Matrix by Nucleus Research provides a snapshot of the LCAP market, assessing vendors based on the usability and functionality of their solutions. This assessment helps customers and prospects understand the competitive landscape, highlighting areas where vendors differentiate themselves and where significant product investments are being made.
Zoho Creator Leader in LCAP
In the 2023 LCAP Technology Value Matrix, Zoho emerges as a leading figure, courtesy of its Zoho Creator platform. This platform distinguishes itself by providing low-code and no-code development tools tailored to both professional and citizen developers. Zoho Creator is lauded for its affordability and its capability to facilitate rapid custom application development without requiring extensive coding knowledge. The platform is versatile, supporting both cloud and on-premises deployment, and offers flexibility in application deployment, including standalone applications or as extensions of the Zoho suite. Key features that attract users include an intuitive drag-and-drop interface, an integrated database, comprehensive ideation and blueprint design tools, and a broad array of ready-made components and integrations.
Zoho Creator enhances operational efficiency through developer governance, platform compatibility, and auto-scaling across various architectures. It simplifies the creation of forms, pages, dashboards, and reports while improving workflows, customer interactions, and integrations via process mining. The platform stands out for its advanced functionalities, such as drag-and-drop custom AI modeling, augmented reality, and self-service analytics.
In terms of governance, Zoho Creator ensures robust access management through support for SAML, LDAP, and OAuth2, and streamlines integration with other services via ready-to-use REST APIs.
Recent updates and enhancements to Zoho Creator underscore the platform's commitment to innovation and user empowerment:
- Custom AI Modeler as a Microservice: This new feature enables the design, training, and deployment of custom AI models within applications, supporting functions such as keyword extraction, sentiment analysis, prediction, OCR, and object detection.
- Canvas for Zoho Creator: A builder with a drag-and-drop interface for visual data presentation design, offering extensive formatting options and enabling users to create custom layouts and control data visibility.
- Metrics: A centralized dashboard offering insights into user activity trends and anomalies across applications, facilitating quick decision-making through visual data representation.
- Augmented Reality Capabilities: Supporting both marker-based and markerless 3D models, allowing users to incorporate 3D models into applications for interactive AR experiences.
- Blueprint Analytics: Enhances business process management with analytics functionality, enabling users to generate insights from real-time data through graphical reports.
Zoho Creator's continuous enhancements and broad range of functionalities solidify its position as a leader in the LCAP market, offering scalable, flexible, and intuitive solutions for businesses aiming to leverage low-code and no-code development.
🌟 Featured Zoho Creator Blog Posts
- Coding is the future: Answers to the Top 10 Questions
- How to avoid reaching maximum limit on zoho creator iterations?
- Streamlining Business Processes with Blueprints in Zoho Creator
- Creating Multi-Step Forms and Consolidated Reports in Zoho Creator
- Mastering Schedule Workflows: Automating Actions Based on Date Field Values in Forms
What are low-code solutions examples?
Low-code solutions examples include platforms like Zoho Creator, OutSystems, Mendix, and Microsoft Power Apps. These platforms provide visual development interfaces that enable users to create applications with minimal coding, accelerating the development process.
How is low-code industry shaping the future of business?
The low-code industry is shaping the future of business by empowering citizen developers and speeding up application development. It allows business users with no coding experience to create applications, enabling faster innovation, increased agility, and improved digital transformation.
What can you build with low-code?
With low-code, you can build a wide range of applications, including customer relationship management (CRM) systems, workflow management tools, project management platforms, employee portals, and more. The flexibility of low-code platforms allows for customization and scalability to meet specific business needs.
What is the future of low-code platform?
The future of low-code platforms looks promising. As businesses continue to embrace digital transformation, low-code will play a vital role in accelerating application development and enabling citizen developers. The platforms will evolve with new features, integrations, and improved user experiences to cater to evolving business requirements.
Which company uses low-code?
Many companies across industries use low-code platforms to streamline their application development processes. Some notable examples include Siemens, Toyota, Deloitte, Lufthansa, and Liberty Mutual. These companies leverage low-code to accelerate innovation, enhance operational efficiency, and improve customer experiences.
What is low-code strategy?
Low-code strategy refers to an organization's approach to utilizing low-code platforms and methodologies. It involves identifying use cases, establishing governance, training citizen developers, and integrating low-code development into the overall digital transformation strategy. A well-defined low-code strategy can drive innovation, agility, and cost savings.